Transformers are among the most common devices discovered in the electric field. They vary in size from less than one cubic inch to the dimension of rail vehicles. Their ratings can easily vary from milli-volt-amperes (mVA) to giga-volt-amperes (GVA). It is crucial that anyone operating in the electric industry have an understanding of transformer types and connections. This article offers transformers intended for use in single phase installations (hence the term single phase transformers). There are 2 major sorts of single phase transformers, isolation transformers and auto-transformers.
A transformer is a magnetically run equipment that could alter values of voltage, current, and impedance without a change of regularity. Transformers are the most efficient machines known to man. Their effectiveness commonly range from 90 % to 99 % at complete load. Transformers can be broken down in to 3 categories:.
1. Isolation transformers
2. Auto-transformers
3. Current transformers
Values of a transformer are proportional to its turn ratio
All values of a transformer are equal to its turns proportion. This does not mean that the specific number of turns of wire on each winding need to be known to determine various worth?s of voltage and current for a transformer. Exactly what ought to be known is the proportion of turns. As an example, assume a transformer has 2 windings. One winding, the primary, has 1000 turns of wire; and the other, the secondary, has 250 turns of wire. The turns ratio of this transformer is 4 to 1, or 4:1 (1000 turns / 250 turns = 4). This indicates there are four turns of wire on the primary for every one turn of cable on the secondary.
Various formulas can be utilized to discover the values of voltage and current for a transformer. The following is a checklist of basic solutions.
Transformer Formulas
The primary winding of a transformer is the power input winding. It is the winding that is connected to the inbound power quantity. The secondary winding is the load winding, or output winding. It is the edge of the transformer that is connected to the forced load.
?
Isolation transformers

An isolation transformer has its primary and secondary windings electrically separated from each other.
Isolation transformers implies that the secondary winding is physically and electrically separated from the primary winding. There is no electric link in between the primary and secondary winding. This transformer is magnetically paired, not electrically coupled. This line isolation is frequently a very preferable feature. The isolation transformer greatly lowers any voltage spikes that originate on the quantity side before they are moved to the load edge. Some isolation transformers are built with a turns ratio of 1:1. A transformer of this type has the very same input and outcome voltages and is used for the purpose of isolation only.
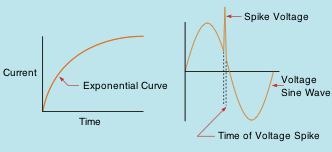
DC through an inductor. Short duration voltage spikes
The reason that isolation transformers can considerably reduce any sort of voltage increases prior to they hit the secondary is due to the rise time of current through an inductor. DC in an inductor increases at an exponential rate. As the current boosts in value, the broadening electromagnetic field cuts through the conductors of the coil and generates a voltage that is opposed to the used voltage. The quantity of induced voltage is symmetrical to the value of modification of current. This merely indicates that the faster current tries to increase, the higher the opposition to that rise is. Spike voltages and current flows are typically of really short duration, meaning that they enhance in value incredibly rapidly. This quick change of value induces the opposition to the change to increase just as swiftly. By the time the spike has actually been moved to the secondary winding of the transformer, it has actually been gotten rid of or substantially lessened.
Auto-transformers
Auto-transformers are one-winding transformers. They utilize the exact same winding for both the primary and secondary. The primary winding is in between stages B and N and has a voltage of 120 volts applied to it. If the turns of cable are counted between points B and N, it can be seen that there are 120 turns of wire. Now presume that the selector change is set to direct D. The load is now connected in between stages D and N. The secondary of this transformer contains 40 turns of cable.
Auto-transformers have only one winding for both the primary ans secondary